Back to Previous Page
PUMPKINSEED
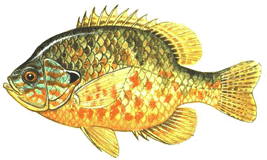
At-a-Glance
- Scientific Name: Lepomis gibbosus
- Found in Illinois: More common in the upper third of Illinois
- State Average: 4.4"
- State Record: 1 lb/ 1.92 oz (2020)
- Best Lures: larval insects, worms, small minnows, leeches.
Habitat:
Pumpkinseed are more commonly found in vegetated ponds and lakes and small rivers. They prefer clear, non-flowing water with abundant vegetation, but can also be found in pools of creeks where vegetation is present. Pumpkinseed are most active during the day throughout the whole water column and are less active and hidden in cover during the night. While they are more low-oxygen tolerant than bluegill, they are less tolerant of warmer water.
Feeding and Habits:
Pumpkinseed mouth parts are able to crush snails so this is a mainstay of their diet. Other favorite foods are larval insects and adult insects that land on the surface.
Reproduction:
Pumpkinseed start to spawn when spring water temperatures begin to reach around 55–63°F. They are solitary nest builders and their well-maintained nests can be seen dotting the shoreline. Males prefer sand or gravel for their nest sites and once these are built, they have an aggressive courtship display to gravid female to come deposit her eggs. Females can deposit eggs over multiple nests and multiple females can deposit eggs in the same nest. Pumpkinseed males, like all sunfish, provide the parental care. Eggs typically hatch 3 days after fertilization while the males guards the nest for 11–14 days.



